TECH TUESDAY: How Ferrari clawed back some pace with low downforce setup at Silverstone


What can we glean from the rear wing set-ups of teams such as Ferrari, Mercedes, Red Bull and Racing Point at the British Grand Prix? In today's Tech Tuesday, Mark Hughes examines the configurations the teams used and how that contributed to their eventual pace, with technical illustrations from Giorgio Piola...
A look at the various rear wing levels chosen by the teams for Silverstone tells a very interesting story. This circuit has now become a low-downforce track in terms of the ideal set-up.
READ MORE: The Winners and Losers of the 2020 British Grand Prix
A few years ago – before the introduction of the more aerodynamically powerful regulations of 2017 – it was more of a downforce track, in that the ultimate lap time tended to be derived from a relatively conventional high-level of rear wing.
But now the cars generate so much downforce from their bigger, more powerful aerodynamic surfaces that they can go through corners such as Copse flat out. No longer are cars with higher rear wing settings faster through such corners.
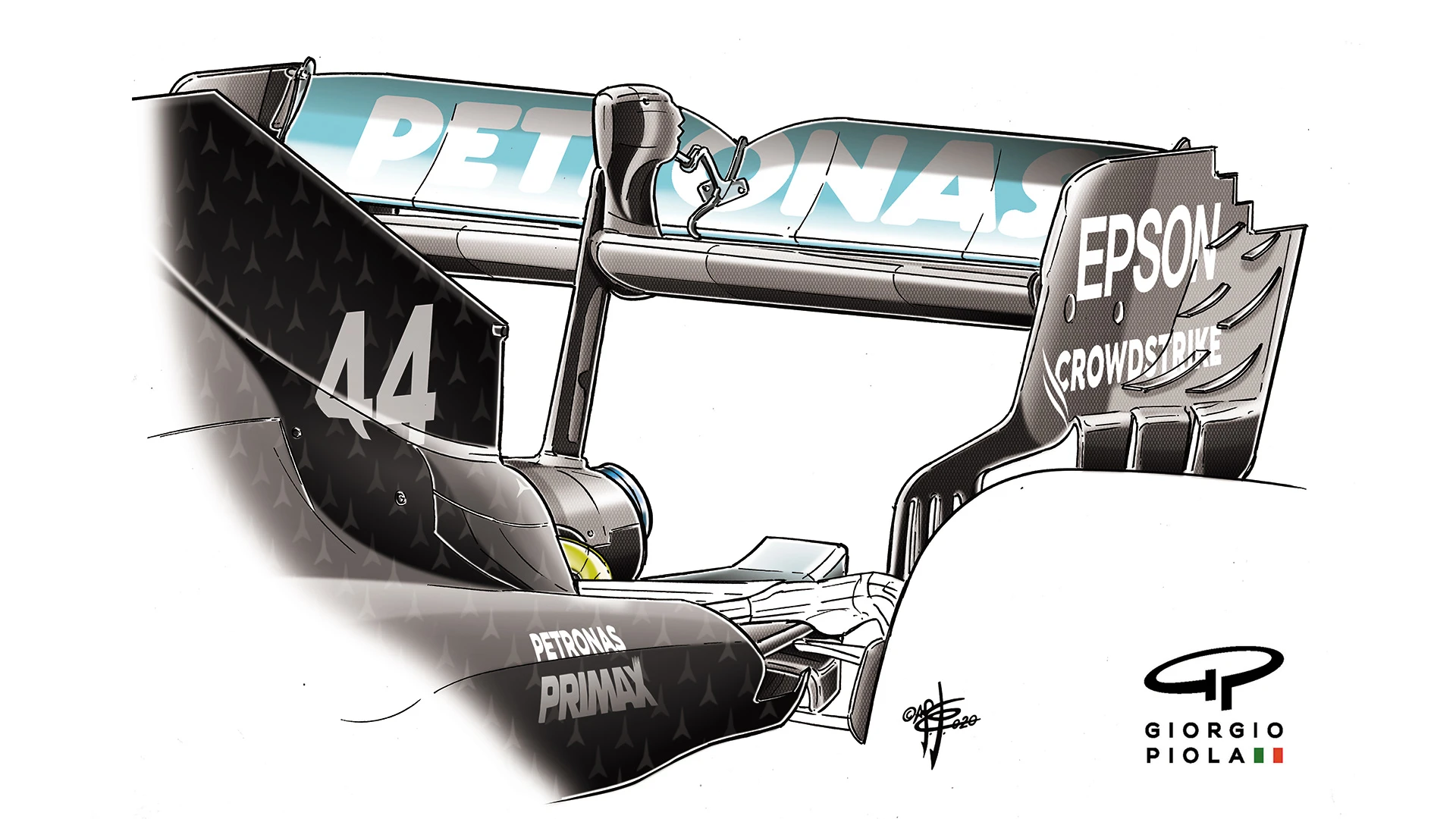
Instead, their speed through those corners is determined solely by how fast they are arriving at them. So for this year Silverstone was the venue at which we saw the teams’ low-downforce packages for the first time.
There is still a trade-off to be made over the lap, however. The slower sections of the track such as the Village loop, the Brooklands-Luffield section and Vale-Club will still favour downforce over drag. Hence, there was a variation between the teams in the choices of just how much downforce to take off.
WATCH: The best team radio from the British GP, including grumpy Raikkonen and Hamilton’s last lap
Ferrari went the most extreme with their low-downforce package, as befitting their shortfall of horsepower. The flap is physically smaller than the others but there they retained a small gurney flap.
The optimum wing level for lap time will always be lower when the car has less horsepower to push it through the air. Because the drag squares with speed, the last few km/h come at a disproportionately high cost in drag and therefore a less powerful engine will tend to suggest a small rear wing.
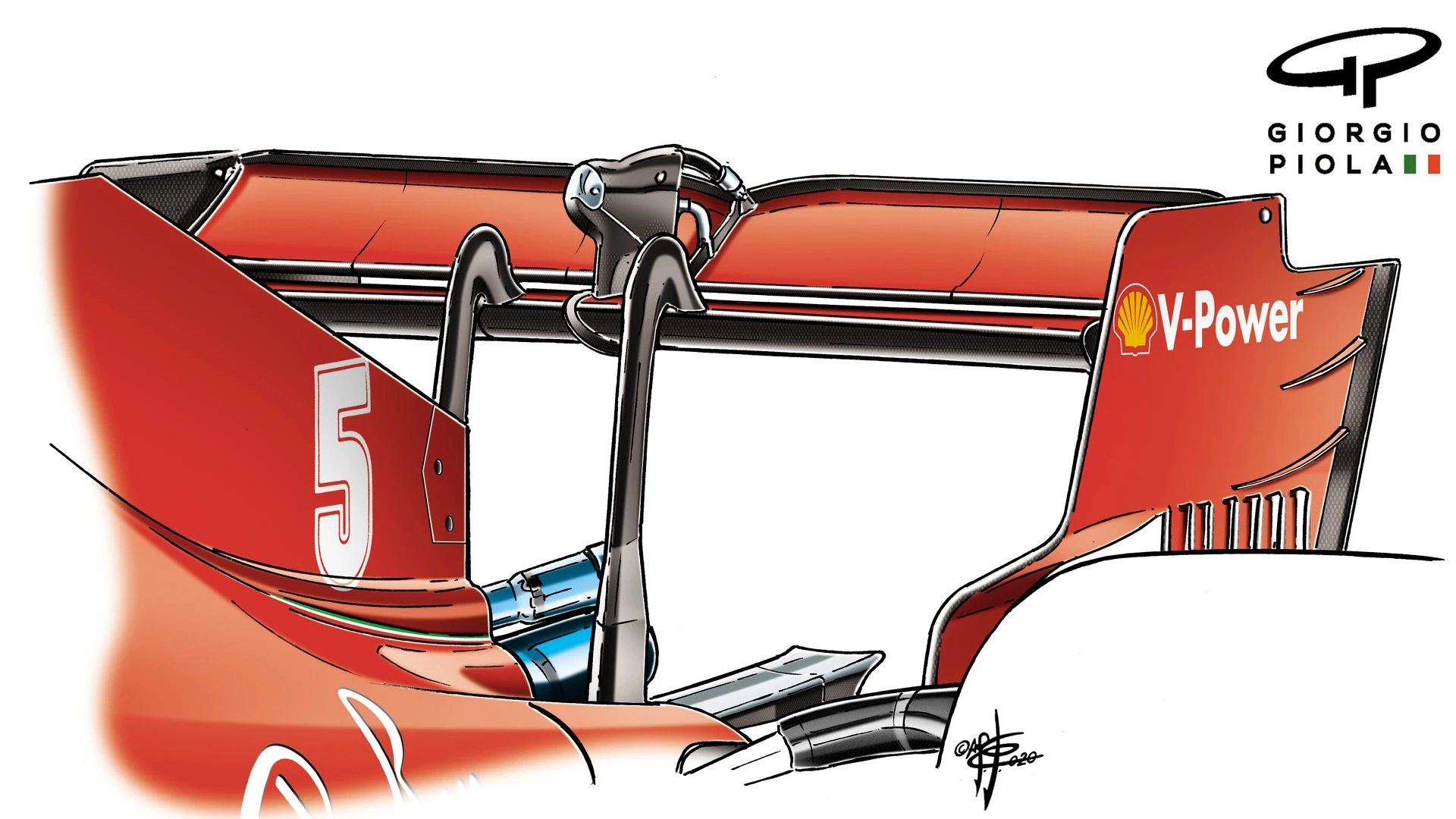
Ferrari’s rear wing was the smallest at Silverstone – and this moved them up from their previous solid last place in the trap speeds to about halfway. It proved a good solution for the team and helped Charles Leclerc qualify on the second row, the foundation of his drive to third in the race.
Mercedes chose probably the second-lowest wing level of the top teams. With the most powerful engine, they were still top of the speed trap. The previous T-wing has been deleted and the flap no longer carries the gurney flap that boosts low-speed downforce but costs drag at higher speeds.
The Ross Brawn column: Why I’d have made the same call as Red Bull on Verstappen’s pit stop
The big reduction in wing levels for Red Bull can be seen quite clearly in the comparison of their Hungarian Grand Prix wing with the circled Silverstone wing. Not only is the wing flap itself smaller and running less of a flap angle, but the endplate is also the lower-drag version (also used in Austria).
The Red Bull RB16 inherently seems to carry more drag than the Mercedes and this together with not quite as extreme a solution (it still carried gurney flaps) saw Max Verstappen just 11th-fastest through the speed trap in qualifying (Hamilton was first, Leclerc eighth).

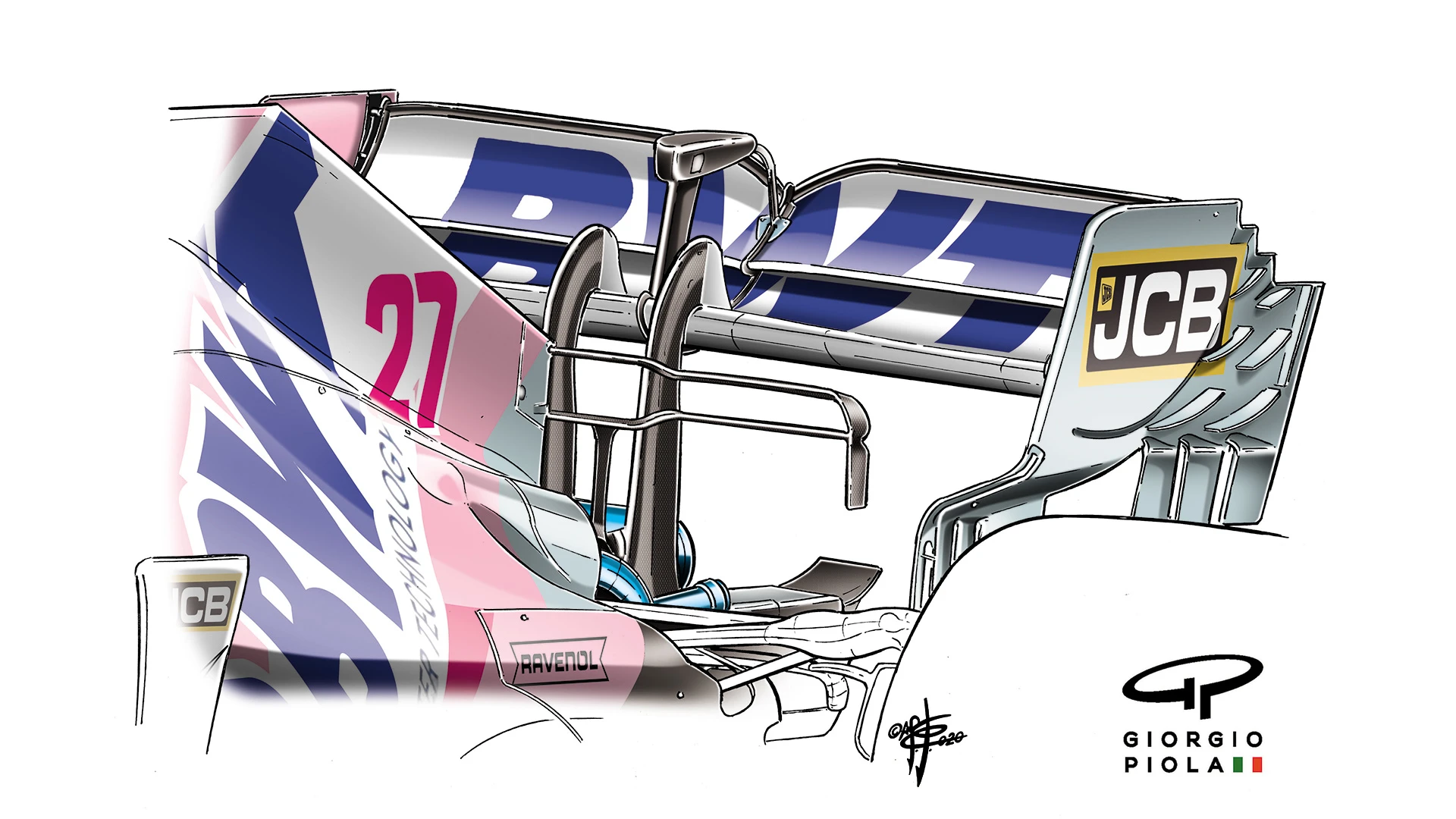
Intriguingly, Racing Point ran a conventional rear wing level at Silverstone, very much off-trend. In previous races the RP20 was among the quickest cars through the speed trap but at Silverstone Lance Stroll was only seventh-quickest despite the benefit of the most powerful engine. It was notable in the race that Stroll was unable to pass cars in front of him and later lost positions to a Renault, an AlphaTauri and a Red Bull.
That would begin to suggest why the Racing Point wasn’t perhaps as competitive around Silverstone as had been expected.
Next Up
Related Articles
 F1 Fantasy strategies for China and Japan
F1 Fantasy strategies for China and Japan Natalia Granada completes the 2026 F1 ACADEMY grid
Natalia Granada completes the 2026 F1 ACADEMY grid Ferrari hope to put Mercedes ‘under more pressure’ in China
Ferrari hope to put Mercedes ‘under more pressure’ in China UnlockedQUIZ: 10 tricky questions on F1 history in China
UnlockedQUIZ: 10 tricky questions on F1 history in China Russell clinches pole in China Sprint Qualifying
Russell clinches pole in China Sprint Qualifying Albon insists Williams have 'clear strategy' to improve
Albon insists Williams have 'clear strategy' to improve